
by Precision Environments | Jun 18, 2024 | Cleanroom Blog, Cleanroom News, News & Resources, Press Releases
On June 3, 2024, employees from Precision Environments delivered a monetary donation and 2 SUV loads of breakfast bars and cereal, microwavable meals and soups, and juices to the Churches Active in Northside’s (CAIN) Rainbow Choice Food Pantry on Hamilton Avenue in Northside. The food will be distributed to the unhoused and to children who don’t have access to regular meals due to school being out for the summer. Precision Environments’ organizer, Beth Clark, commented, “We do our food drive at this time of year since most people do it around Thanksgiving and Christmas. These items are needed all year round.”

by Jeff Meek | Jun 18, 2024 | Cleanroom Blog, Jeff Meek
In industries like pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and medical devices, cleanrooms are essential for maintaining the integrity of processes and products. For cleanrooms requiring the control of microorganisms, often involving sporicidal agents and other chemicals, careful design is crucial to manage contamination risks effectively.
by Jeff Meek | May 24, 2024 | Cleanroom Blog, Jeff Meek
Cleanrooms are critical environments where the slightest contamination can compromise product quality, research integrity, or even human health. Whether it’s pharmaceuticals, electronics, biotechnology, or aerospace, maintaining precise cleanliness standards is of the highest importance. Key aspects of cleanroom design are air filters and Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems, which are engineered to remove particles and pollutants
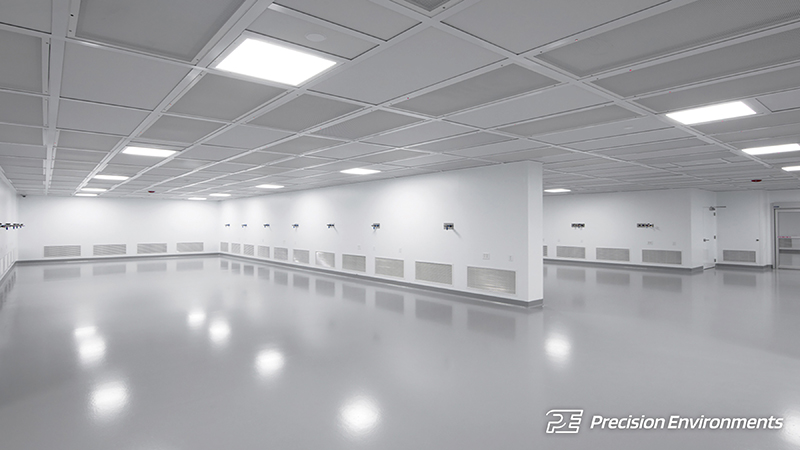

by Jeff Meek | Apr 22, 2024 | Cleanroom Blog, Jeff Meek
Designing and building an efficient and hygienic cleanroom environment requires careful consideration of the wall system you use. Cleanroom wall panels provide the framework for your controlled environment, ensuring it meets strict standards of cleanliness and functionality. There are a range of wall panel systems tailored to different cleanroom requirements. Let’s explore the options available and the advantages they offer.
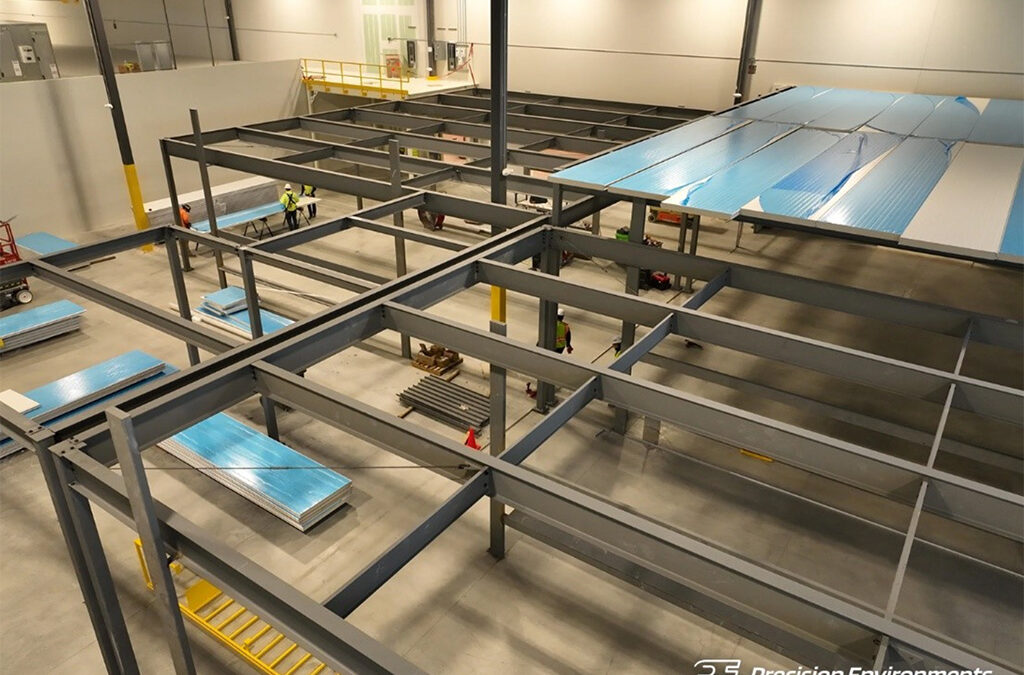

by Jeff Meek | Apr 6, 2024 | Cleanroom Blog, Cleanroom Knowledge Base, Jeff Meek
Cleanrooms are critical environments used in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, electronics manufacturing, and aerospace. Maintaining the highest levels of cleanliness and controlling environmental factors like particulate matter, temperature, humidity, and pressure is essential for the success of operations within cleanrooms. However, achieving these stringent requirements relies on the structural support systems that uphold the integrity of the cleanroom environment. In this blog post, we will look at some ways cleanroom systems are structurally supported.
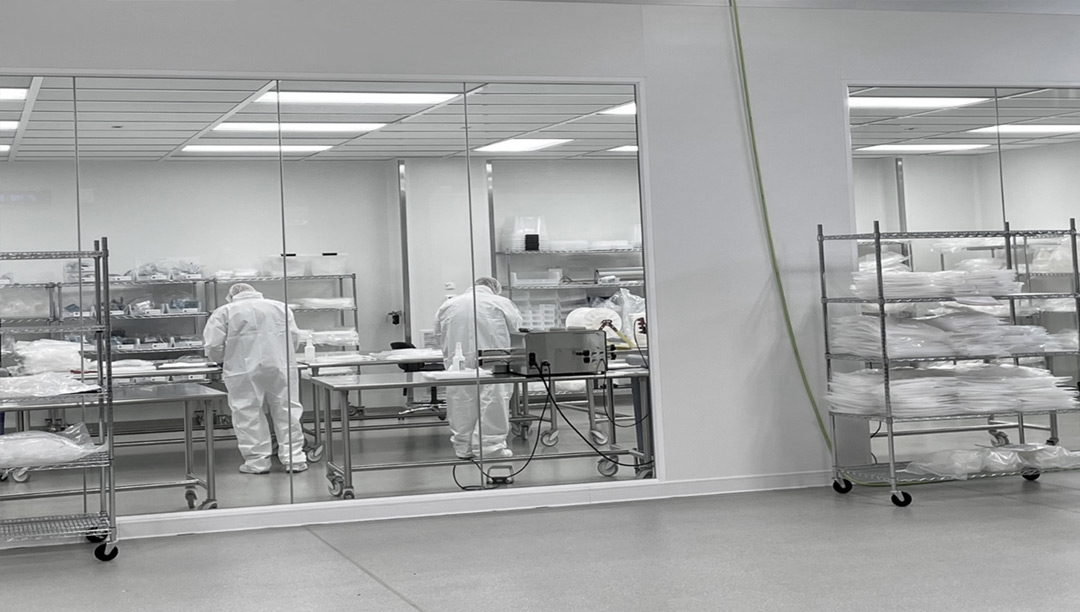

by Jeff Meek | Mar 26, 2024 | Cleanroom Blog, Cleanroom Knowledge Base, Jeff Meek
Cleanrooms serve as critical environments across diverse industries, ensuring product quality, safety, and compliance with regulatory standards. Let us explore several types of cleanrooms and give a quick look at their applications:





